Hurricane Forecast Analysis
Hurricane forecasts are an essential tool for emergency managers, coastal residents, and anyone else who may be affected by a hurricane. They provide critical information about the expected path, intensity, and timing of a hurricane, which can help people make informed decisions about how to prepare and stay safe.
Hurricane forecasts are essential for preparing for and mitigating the impacts of these powerful storms. In recent years, Puerto Rico has experienced several devastating hurricanes, including Hurricane Maria in 2017, which caused widespread damage and loss of life. By staying informed about hurricane forecasts, Puerto Ricans can take steps to protect themselves and their communities from the potential impacts of these storms.
For more information on hurricane preparedness in Puerto Rico, visit puerto rico hurricane.
Key Components of a Hurricane Forecast
The key components of a hurricane forecast include:
- Track: The predicted path of the hurricane, including the expected landfall location and time.
- Intensity: The expected maximum sustained wind speed of the hurricane, which is used to determine the hurricane’s category on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
- Timing: The expected time of arrival of the hurricane at various locations along its track.
- Size: The expected size of the hurricane, including the diameter of the area that will be affected by tropical storm-force winds.
- Storm surge: The expected height of the storm surge, which is the rise in sea level caused by the hurricane’s winds and low pressure.
- Rainfall: The expected amount of rainfall that the hurricane will produce, which can lead to flooding and other hazards.
Forecasting Models
There are a variety of different forecasting models that are used to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes. These models use a variety of data, including observations from weather stations, satellites, and radar, to create a computer simulation of the hurricane’s behavior. The most commonly used forecasting models include:
- Global Forecast System (GFS): A global model that is run by the National Weather Service (NWS).
- Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF): A hurricane-specific model that is also run by the NWS.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): A global model that is run by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts.
- Consolidated Tropical Cyclone Guidance (CTCG): A consensus forecast that combines the results of several different forecasting models.
Accuracy and Limitations
Hurricane forecasts have become increasingly accurate over the past few decades, but they are still not perfect. The accuracy of a hurricane forecast depends on a number of factors, including the availability of data, the quality of the forecasting models, and the skill of the forecasters.
One of the biggest limitations of hurricane forecasts is that they are often not able to predict the exact path of a hurricane. This is because hurricanes are complex systems that are influenced by a variety of factors, including the interaction of the atmosphere and the ocean. As a result, hurricane forecasts can sometimes be off by hundreds of miles.
Hurricane forecasts are crucial for predicting the path and intensity of these storms, allowing for timely preparations and evacuations. For the latest updates on the beryl hurricane track , refer to reliable weather sources for accurate information. These forecasts provide valuable insights into the potential impact of hurricanes, helping communities stay informed and take necessary precautions.
Another limitation of hurricane forecasts is that they are not able to predict the exact intensity of a hurricane. This is because the intensity of a hurricane is determined by a number of factors, including the temperature of the ocean water and the amount of wind shear in the atmosphere. As a result, hurricane forecasts can sometimes be off by several categories.
Despite these limitations, hurricane forecasts are still an essential tool for emergency managers, coastal residents, and anyone else who may be affected by a hurricane. They provide critical information about the expected path, intensity, and timing of a hurricane, which can help people make informed decisions about how to prepare and stay safe.
Factors Influencing Hurricane Formation and Intensity
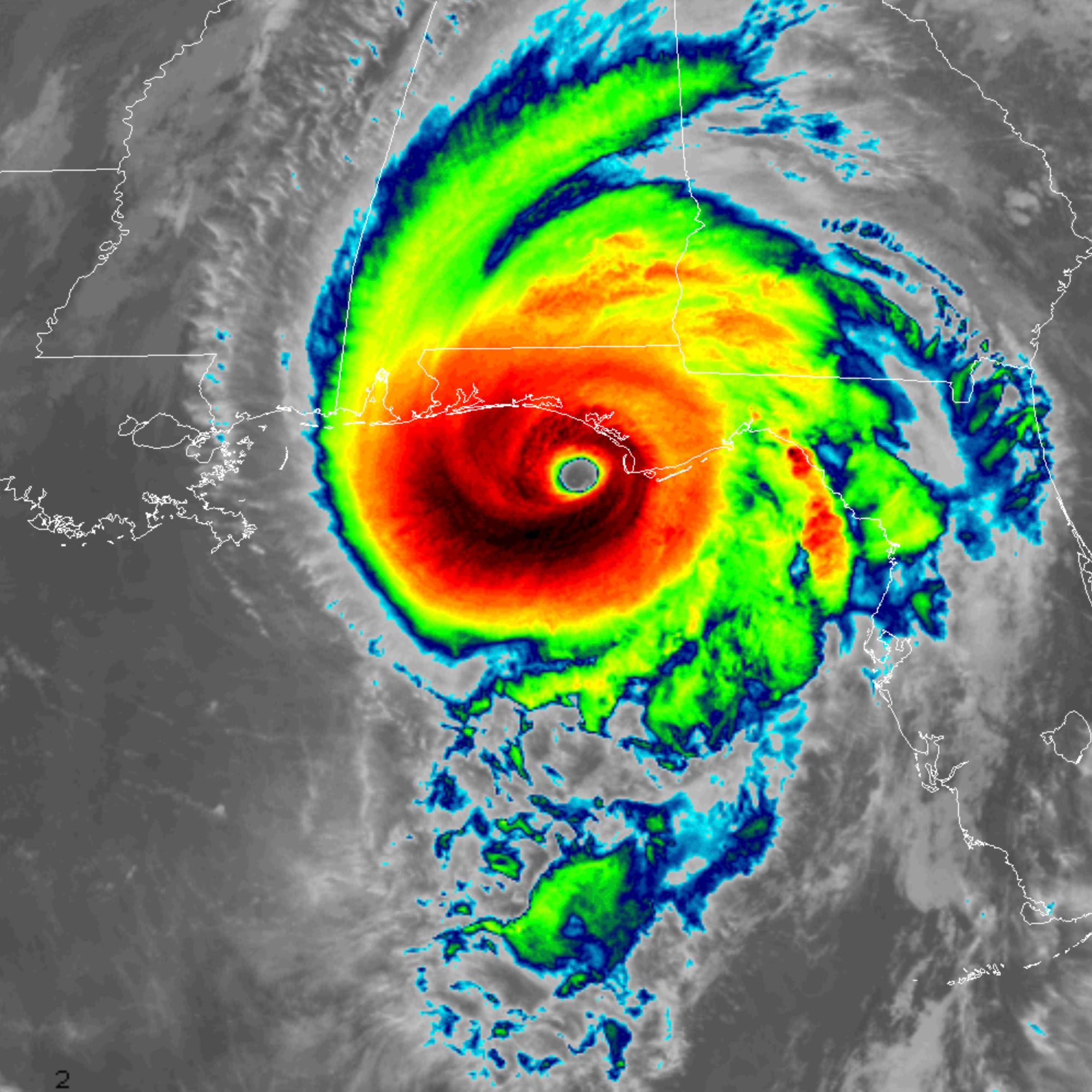
Hurricanes are massive, rotating storms that form over warm ocean waters. They are fueled by the heat and moisture released from the ocean, and they can cause widespread damage and loss of life. The formation and intensity of hurricanes are influenced by a number of factors, including ocean temperature, wind shear, and atmospheric pressure.
Ocean Temperature
The ocean temperature is one of the most important factors in hurricane formation. Hurricanes require warm ocean waters to form and develop. The warm water provides the energy that fuels the storm. The ocean temperature must be at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit for a hurricane to form. The warmer the water, the more energy the storm will have.
Wind Shear
Wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction between two levels of the atmosphere. Wind shear can disrupt the formation and development of hurricanes. Strong wind shear can prevent a hurricane from forming or cause it to weaken. The wind shear must be less than 10 knots for a hurricane to form. The stronger the wind shear, the less likely a hurricane is to form or develop.
Atmospheric Pressure
The atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air above a given point. The atmospheric pressure must be low for a hurricane to form. The lower the atmospheric pressure, the more likely a hurricane is to form. The atmospheric pressure must be less than 1000 millibars for a hurricane to form. The lower the atmospheric pressure, the stronger the hurricane will be.
Impacts and Preparedness: Hurricane Forecast

Hurricanes can have a devastating impact on coastal communities, causing widespread damage and loss of life. The primary hazards associated with hurricanes include storm surge, flooding, and wind damage.
Storm Surge
Storm surge is a wall of water that can reach heights of up to 20 feet or more. It is caused by the strong winds of a hurricane pushing water towards the shore. Storm surge can cause extensive flooding, destroying homes and businesses and making roads impassable.
Flooding, Hurricane forecast
Hurricanes can also cause flooding from heavy rainfall. This can lead to rivers and streams overflowing their banks, as well as flash flooding in low-lying areas. Flooding can damage homes and businesses, as well as infrastructure such as roads and bridges.
Wind Damage
The high winds of a hurricane can cause widespread wind damage. This can include damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, as well as downed trees and power lines. Wind damage can also lead to power outages, which can disrupt essential services such as water and communication.
Hurricane Preparedness
There are a number of things that individuals and communities can do to prepare for hurricanes. These include:
- Developing an evacuation plan and practicing it with your family.
- Assembling an emergency kit that includes food, water, first aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Securing your home by boarding up windows and doors and bringing in loose objects.
- Staying informed about the hurricane and following the instructions of local officials.
Role of Technology
Technology plays an important role in hurricane forecasting and warning systems. Weather satellites and radar systems are used to track hurricanes and predict their path and intensity. This information is used to issue hurricane warnings and advisories, which help people to prepare for and evacuate from the storm.
In addition, technology is also being used to develop new ways to mitigate the impacts of hurricanes. For example, researchers are developing new types of storm surge barriers and flood control systems that can help to protect coastal communities from the worst effects of hurricanes.